Have you ever heard of mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA but do not know what it is? In this blog, we will be discussing what mitochondrial DNA is and its functions, structure, and how it is passed down. We will also discuss how it is used in research and medicine, the benefits, and potential disadvantages of understanding mtDNA. By the end of this blog, you will have all the information you need to know.
Introduction
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a type of DNA that is located outside the nucleus in the mitochondria and is inherited solely from the mother. Mitochondrial DNA is used to integrate energy metabolism to generate energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). It is also used in the production of proteins, which are involved in many cellular processes.
mtDNA has been the subject of intensive scientific research for over two decades. Scientists have discovered that mitochondrial DNA can be used to trace matrilineal (mother-line) ancestry, as well as to diagnose and treat diseases through gene therapy. It is also being used to understand the evolutionary history of humans and to discover new treatments for diseases.
Scientists have been studying mitochondrial DNA for a long time and have found many uses for it. Mitochondrial DNA can be used to trace one’s ancestry, as well as to diagnose and treat diseases through gene therapy.
mtDNA in detail
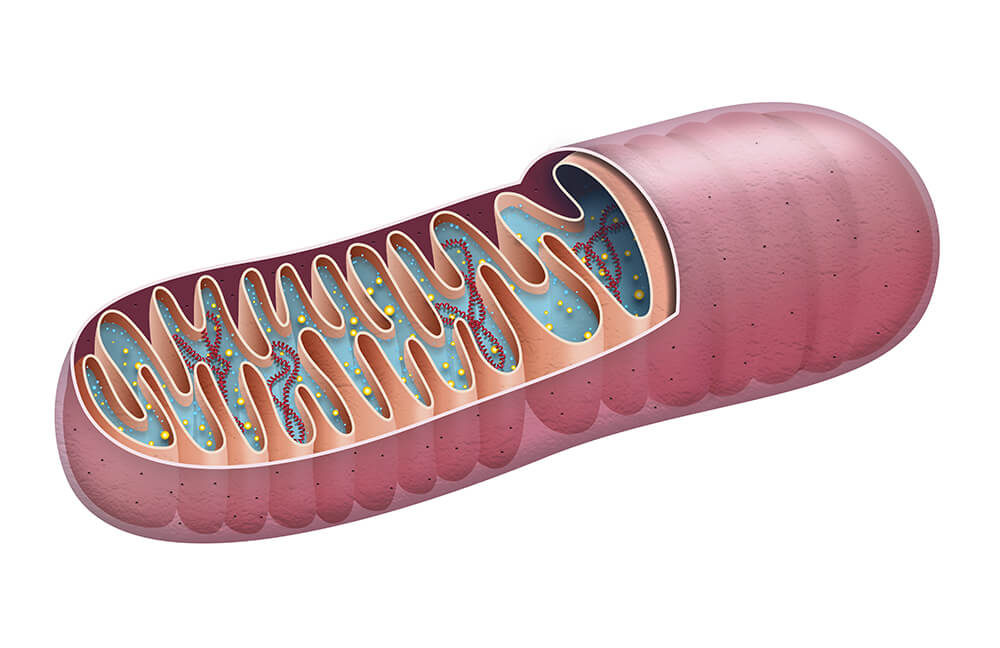
mtDNA is a double-stranded, circular molecule of 16,596 bp (base pair). Mitochondrial DNA contains 37 genes, which are responsible for coding proteins, tRNA, and rRNA. These proteins, tRNA, and rRNA are essential for the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and other cellular functions.

Mitochondrial DNA is distinct from nuclear DNA, which is found in the nucleus of the cell. Mitochondrial DNA is only inherited from the mother, making it a powerful tool for tracing ancestry.
Mitochondrial Function
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has several functions within the cell. Firstly, it is responsible for the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the molecule responsible for energy production which powers all cells. It is also responsible for the production of proteins, tRNA, and Mitochondrial rRNA, which are essential for cellular function. Additionally, mitochondrial DNA plays an important role in the regulation of cellular metabolism.
Mitochondrial DNA is also involved in the production of proteins, which are involved in many cellular processes. These proteins can be used to regulate gene expression, which can lead to changes in cell growth and development. Additionally, they can be used to regulate the cell’s response to environmental stressors.
Structure
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a double-stranded, circular molecule. It is composed of 37 genes, which are responsible for coding proteins, tRNA, and rRNA. The genes are organized into two regions: the control region, which contains the regulatory sequences, and the coding region, which contains the genes for the proteins, tRNA, and rRNA.
The structure of mitochondrial DNA is highly conserved, meaning that the structure of mitochondrial DNA in different species is very similar. This is because it is passed down from mother to offspring, with only minor mutations in mitochondrial occurring over time. This makes mitochondrial DNA an ideal tool for tracing human ancestry.
How is Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Passed Down?
Mitochondrial DNA is only inherited from the mother, making it a powerful tool for tracing ancestry. The mitochondria are inherited in the egg cell, which is passed down from the mother to the offspring. This means that the mitochondrial DNA in each generation is identical, with only minor mutations occurring over time. Researchers can use mitochondrial DNA to learn more about human ancestry by tracing it back many generations.
Mitochondrial DNA is passed down from the mother, grandmother, great-grandmother, and so on. This allows researchers to learn a lot about a person’s ancestry.How is mtDNA Used in Research?
Mitochondrial DNA s a powerful tool for researchers to trace maternal lineage. By comparing the DNA of different individuals, researchers can trace the evolution of human populations over hundreds of generations. This can help researchers to understand the evolution of human populations, as well as to identify populations that are more closely related to one another.

It is also being used to study the evolution of other organisms, such as plants and animals. By studying the DNA of different species, researchers can gain insight into their evolution and the evolutionary relationships between different species.
How is mtDNA Used in Medicine?
mtDNA is being used in medicine to diagnose and treat diseases. By comparing the DNA of different individuals, researchers can identify genetic mutations in mtDNA that are associated with certain diseases. This can help doctors to diagnose diseases and to identify potential treatments.
It is also being used in personalized medicine, which is a type of medicine that uses an individual’s genetic information to provide treatments tailored to their specific needs. By studying an individual’s mitochondrial DNA, doctors can identify genetic mutations that may be causing their disease and tailor treatments to their specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is responsible for the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and other cellular functions. It is also used to trace matrilineal ancestry, as well as to diagnose and treat diseases.
Understanding it can have many benefits, such as the ability to trace human ancestry and to identify genetic mutations that may be causing diseases. However, there are also potential disadvantages, such as the potential for misuse of the information and a lack of understanding of other genetic factors. This is why it is important for submitting your DNA to a trustworthy company.
Mitochondrial DNA is a critical part of all cells and is essential for understanding human evolution. Mitochondrial DNA is also a powerful tool for treating diseases and gaining insights into your ancestry.